Difference between revisions of "Arduino"
| Line 37: | Line 37: | ||
=== Ethernet === | === Ethernet === | ||
| − | The IP address of the board is specified in it's sketch (see [[#Arduino | + | The IP address of the board is specified in it's sketch (see [[#Arduino Programming|Arduino Programming]]) and the default port is 23. |
== Arduino Configuration == | == Arduino Configuration == | ||
Revision as of 12:23, 9 January 2014
Arduino is a microcontroller platform and development tools combined into an easy-to-use, standardized and inexpensive architecture that can greatly enhance the physical input/output capabilities of HSYCO.
HSYCO supports Arduino through an open source library installed in the Arduino IDE. This library implements a bidirectional communication protocol with HSYCO. A sketch in Arduino that allows HSYCO to directly read and control any of the digital and analog pins on any Arduino board is only a few lines long, and is provided as a built-in example in the HSYCO library. HSYCO supports Arduino Uno, Arduino Ethernet, Arduino Due and other compatible boards. The connection is serial, usually over the USB port, or TCP over the Ethernet. The Arduino I/O Server provides for datapoints to be used in the EVENTS language and Java to read and control Arduino pins, but also to exchange custom messages between your sketch in Arduino and HSYCO applications.
Contents
Communication
Arduino can be connected to HSYCO through a USB cable (serial communication) or via Ethernet depending on the model.
Serial (USB)
The comm port ID depends on your HSYCO server configuration. It should be "ttyACM0" if there are no other devices connected to the USB ports.
These are the default serial communication parameters used by the HSYCO library:
| Baud rate | 115200 |
| Data bits | 8 |
| Stop bit | 1 |
| Parity | none |
| Flow control | none |
Ethernet
The IP address of the board is specified in it's sketch (see Arduino Programming) and the default port is 23.
Arduino Configuration
IDE Configuration
Before you start writing sketches using the Arduino IDE, you should copy the HSYCO or HSYCONET libraries in the libraries directory.
On Mac, the libraries directory is in your home directory, Documents/Arduino/libraries.
On Linux it is in the shetchbook directory of your home directory.
On Windows the folder is in My Documents\Arduino.
Use the HSYCO library when you are connecting Arduino and HSYCO via a serial/USB cable, or HSYCONET if using TCP over an Ethernet network.
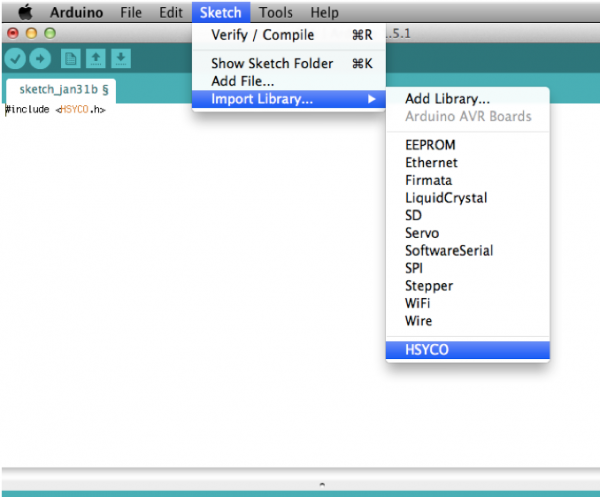
Quit and reopen the Arduino IDE to make it aware of the new library. After restarting the Arduino IDE, you can create a new custom sketch with File → New, then Sketch → Import Library → HSYCO.
Arduino Programming
The HSYCO or HSYCONET library in Arduino will map all I/O pins, and the most relevant I/O functions in Arduino, to datapoints that you can use to set output pins and read input pins of the Arduino board.
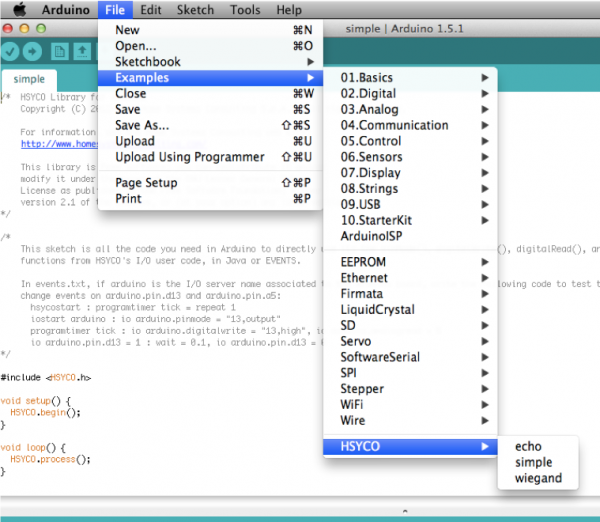
If you only need to directly control Arduino’s pins from HSYCO EVENTS or Java, without any custom sketch code in Arduino, select File → Examples → HSYCO → simple.
Upload the simple sketch to your board, and you are ready to use Arduino from HSYCO.
This sketch is all the code you need in Arduino to directly call the pinMode(), digitalWrite(), digitalRead(), analogRead() and analogWrite() functions from HSYCO.
Simple sketch using the HSYCO library (serial communication):
#include <HSYCO.h>
void setup() {
HSYCO.begin();
}
void loop() {
HSYCO.process();
}
Simple sketch using the HSYCONET library (Ethernet communication):
#include <HSYCONET.h>
#include <Ethernet.h>
#include <SPI.h>
byte mac[] = { 0xDE, 0xAD, 0xBE, 0xEF, 0xFE, 0xED };
IPAddress ip(192, 168, 1, 177);
IPAddress subnet(255, 255, 255, 0);
IPAddress gateway(192, 168, 1, 1);
void setup() {
Ethernet.begin(mac, ip, gateway, subnet);
HSYCONET.begin();
}
void loop() {
HSYCONET.process();
}