Difference between revisions of "Domino"
| Line 127: | Line 127: | ||
|} | |} | ||
| − | == | + | == The Device Configuration Database == |
| − | The | + | The systemtopo.txt file contains the list of all devices and their individual input, output and virtual data points that could be directly associated to graphic object in the Web-based user interface. |
| − | + | This file can be filled manually or automatically by HSYCO at start-up. To enable automatic discovery and automatic generation of devices’ information in the systemtopo file, use the ''inputdiscovery'', ''outputdiscovery'' and ''virtualdiscovery'' options in the hsyco.ini configuration file. The default behavior is to only discover devices with output data points. | |
| − | This file | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | The | ||
| + | This is an example of an automatically generated systemtopo.txt file: | ||
<pre> | <pre> | ||
| − | + | (devices) | |
| − | + | domino.o10.1 : LIGHT ; LIGHT | |
| − | + | domino.o6.1 : LIGHT ; DIMMER | |
| − | + | domino.o7.2 : LIGHT ; LIGHT | |
| − | + | domino.o7.1 : LIGHT ; DIMMER | |
| − | + | domino.o9.2 : AUTOM ; VSHUT | |
| − | + | domino.o5.4 : LIGHT ; LIGHT | |
| − | + | domino.o9.1 : AUTOM ; VSHUT | |
| − | + | domino.o5.3 : LIGHT ; LIGHT | |
| − | + | domino.o5.2 : LIGHT ; LIGHT | |
| − | + | domino.o5.1 : LIGHT ; LIGHT | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
| − | + | You should then manually add comments and other optional parameters: | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
<pre> | <pre> | ||
| − | + | (devices) | |
| − | + | domino.o10.1 : LIGHT ; LIGHT; main entrance light | |
| − | + | domino.o6.1 : LIGHT ; DIMMER; lobby dimmer | |
| − | + | domino.o7.2 : LIGHT ; LIGHT; kitchen workbench | |
| + | domino.o7.1 : LIGHT ; DIMMER; kitchen main dimmer | ||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
| − | |||
| − | + | == DFCP Virtual Data Points and Registers == | |
| − | + | The DFCP implements 2032 virtual points for binary (on/off) data and 1024 registers for positive scalar values (0-65535). All the virtual points and the registers can optionally generate I/O events. You can also write to the virtual data points and registers using the IO action in EVENTS or ioSet() method in Java. | |
| + | You cannot directly control the DFCP virtual data points and registers using GUI objects. | ||
| + | To enable polling of the current state of the DFCP’s virtual data points, enable the virtualpoints options in hsyco.ini. | ||
| + | To enable polling of the current state of the DFCP’s registers, enable the registers options in hsyco.ini. | ||
| + | If you only have to write to virtual points or registers, enabling polling is not strictly required. | ||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| Line 199: | Line 169: | ||
!R/W | !R/W | ||
!Description | !Description | ||
| − | |||
|- | |- | ||
| − | |rowspan="2" | | + | |rowspan="2"|v0.<n> |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
|0 | |0 | ||
| − | | | + | |RW |
| − | | | + | |virtual data point <n> off (<n>: 1-2032) |
|- | |- | ||
|1 | |1 | ||
| − | | | + | |RW |
| − | | | + | |virtual data point <n> on (<n>: 1-2032) |
| − | |||
| − | |||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |r0.<n> |
| − | | | + | |<x> |
| − | + | |RW | |
| − | + | |register <n> off (<n>: 0-1023) set to value <x> (<x>: 0-65535) | |
| − | |||
| − | | | ||
| − | | | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
|- | |- | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | | | + | |} |
| − | + | == Datapoints == | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | !ID | ||
| + | !Value | ||
| + | !R/W | ||
| + | !Description | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | |rowspan="2" | | + | |rowspan="2" |connection |
| − | | | + | |online |
|R | |R | ||
| − | | | + | |connection established |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |offline |
|R | |R | ||
| − | | | + | |HSYCO can't connect to the panel |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
|- | |- | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
|} | |} | ||
| Line 662: | Line 212: | ||
== User Interface == | == User Interface == | ||
| − | === | + | === Object === |
{{:Inim_(UI Object)}} | {{:Inim_(UI Object)}} | ||
| Line 675: | Line 225: | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
|} | |} | ||
=== USER Commands === | === USER Commands === | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| Line 894: | Line 235: | ||
!Action | !Action | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
|} | |} | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
Revision as of 13:48, 29 January 2014
The DOMINO system is DUEMMEGI’s proprietary bus architecture for home automation. HSYCO fully integrates with this system through the DFCP control and gateway module, and its FXP-XT serial communication protocol. A serial connection between the DFCP and the HSYCO SERVER is required for the integration, either directly through the server’s RS-232 port or via the RS-232 port of a supported serial to IP gateway, including the WEBS module.
Contents
Communication
Employ a DE-9 (often called DB-9) male-female RS-232 straight cable to connect the RS-232 DFCP port to the serial port on HSYCO SERVER or serial gateway. The communication baud rate can be set to 9600, 38400, 57600 or 115200 bps, according to the DFCP serial port settings. The protocol requires 8bit data, no parity, one stop bit, no flow control. A speed of 115200 bps is recommended to achieve good performance, particularly when the number of devices connected to the bus is large.
HSYCO Configuration
Options
| ID | Default | Values | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| startupevents | false | true | generate IO events also during the driver’s start-up phase |
| false | start generating events only after HSYCO is aligned with the current status of the system | ||
| inputdiscovery | false | true | auto-detects DOMINO’s input devices as configured in the DFCP, and automatically creates the list of all detected devices and individual data points in the systemtopo.txt file. Should be enabled to allow the automatic update of (button) objects’ states |
| false | auto-detect for input devices is disabled | ||
| outputdiscovery | true | true | auto-detects DOMINO’s output devices as configured in the DFCP, and automatically creates the list of all detected devices and individual data points in the systemtopo.txt file. Should be enabled to allow the automatic update of (button) objects’ states |
| false | auto-detect for output devices is disabled | ||
| virtualdiscovery | false | true | auto-detects DOMINO’s virtual points for input and output devices as configured in the DFCP, and automatically creates the list of all detected virtual data points in the systemtopo.txt file. Should be enabled to allow the automatic update of (button) objects’ states |
| false | auto-detect for devices’ virtual data points is disabled | ||
| virtualpoints | false | 1...2033 | enables polling for the first n virtual points of the DFCP. Enable this option only if you need to generate I/O events based on these virtual points |
| true | enables polling for all the 2032 virtual points of the DFCP | ||
| false | polling of the DFCP virtual data points is disabled | ||
| registers | false | 1...1024 | enables polling for registers R0-Rn of the DFCP. Enable this option only if you need to generate I/O events based on these registers |
| true | enables polling for registers R0-R127 of the DFCP | ||
| false | polling of the DFCP registers is disabled | ||
| powerdisplay | false | true | enables polling for registers R0-Rn of the DFCP. Enable this option only if you need to generate I/O events based on these registers |
| ≥ 0 (DFANA address) | enables the automatic display in the GUI of the total real power measured by a DFANA module connected to this DFCP. Note that, if you have more than one DFCP gateway, you should enable this option for one gateway only | ||
| false | power display disabled for this DFCP | ||
| powersensivity | 50 | ≥ 0 | measured power changes are reported only if the difference from last reading is equal or greater than the power sensivity option, in Watts |
| powerinterval | 1 | ≥ 0 | power polling interval for the DFCC meter, in seconds |
| detectevents | false | true | generate forced events when a device is detected at start-up |
| false | do not generate events when a device is detected at start-up | ||
| toolspassword | string | set this option with a long string (only letters and numbers) password to allow the remote connection of DFCP-IDE and other configuration tools to the DFCP gateways that are connected to HSYCO. For additional security, it is recommended to set this option only when required | |
| language | english | en it fr | language for all messages from the DOMINO system: English, Italian or French |
The Device Configuration Database
The systemtopo.txt file contains the list of all devices and their individual input, output and virtual data points that could be directly associated to graphic object in the Web-based user interface. This file can be filled manually or automatically by HSYCO at start-up. To enable automatic discovery and automatic generation of devices’ information in the systemtopo file, use the inputdiscovery, outputdiscovery and virtualdiscovery options in the hsyco.ini configuration file. The default behavior is to only discover devices with output data points.
This is an example of an automatically generated systemtopo.txt file:
(devices) domino.o10.1 : LIGHT ; LIGHT domino.o6.1 : LIGHT ; DIMMER domino.o7.2 : LIGHT ; LIGHT domino.o7.1 : LIGHT ; DIMMER domino.o9.2 : AUTOM ; VSHUT domino.o5.4 : LIGHT ; LIGHT domino.o9.1 : AUTOM ; VSHUT domino.o5.3 : LIGHT ; LIGHT domino.o5.2 : LIGHT ; LIGHT domino.o5.1 : LIGHT ; LIGHT
You should then manually add comments and other optional parameters:
(devices) domino.o10.1 : LIGHT ; LIGHT; main entrance light domino.o6.1 : LIGHT ; DIMMER; lobby dimmer domino.o7.2 : LIGHT ; LIGHT; kitchen workbench domino.o7.1 : LIGHT ; DIMMER; kitchen main dimmer
DFCP Virtual Data Points and Registers
The DFCP implements 2032 virtual points for binary (on/off) data and 1024 registers for positive scalar values (0-65535). All the virtual points and the registers can optionally generate I/O events. You can also write to the virtual data points and registers using the IO action in EVENTS or ioSet() method in Java. You cannot directly control the DFCP virtual data points and registers using GUI objects. To enable polling of the current state of the DFCP’s virtual data points, enable the virtualpoints options in hsyco.ini. To enable polling of the current state of the DFCP’s registers, enable the registers options in hsyco.ini. If you only have to write to virtual points or registers, enabling polling is not strictly required.
| ID | Value | R/W | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| v0.<n> | 0 | RW | virtual data point <n> off (<n>: 1-2032) |
| 1 | RW | virtual data point <n> on (<n>: 1-2032) | |
| r0.<n> | <x> | RW | register <n> off (<n>: 0-1023) set to value <x> (<x>: 0-65535) |
Datapoints
| ID | Value | R/W | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| connection | online | R | connection established |
| offline | R | HSYCO can't connect to the panel |
User Interface
Object
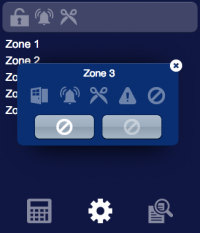
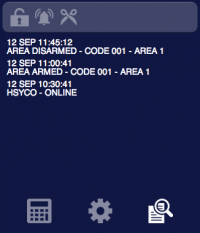
The user interface for the control and supervision of one area of the system, the zones and the visualization of the security log:
The Inim object is listed in the Project Editor’s new object list only when at least one INIM I/O Server is defined.
Parameters
- id - the id assigned to the INIM I/O Server in hsyco.ini. Supports Redirect variables
- area - the number of the area to be addressed. Supports Redirect variables
- pos - the object’s position. Use the pixels or rows and columns coordinates format.
Syntax
(inim <server id>; <area>; <position>)
E.g.
(inim serverid; area; x10y20)
UISET Actions
| ID | Attribute | Set to | |
|---|---|---|---|
USER Commands
| Name | Param | Action |
|---|